Measuring White Blood Cells (Leukocyte) Recruitment Onto Substrates Bearing Vascular Adhesion Molecules
Introduction
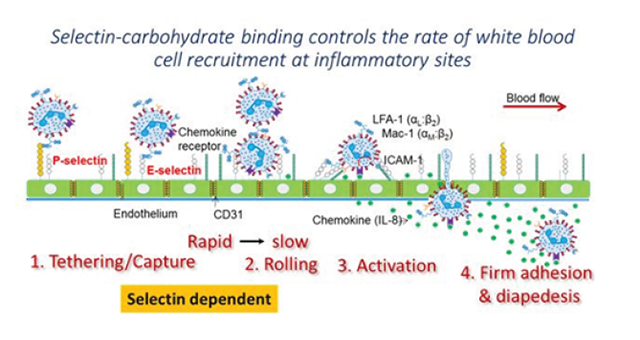
The application of Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) for cell based assays is an emerging research theme. The accessible and easy to change tubing (typical i.d. values ranging from 0.005-0.04" (125-1000 μm)) and ability to change flow rate over a wide range (0.1 μL/min to 3 mL/min) makes Reichert SPR instruments particularly well suited for cell studies. This application note demonstrates the use of the Reichert 2SPR instrument to measure the binding of white blood cells or leukocytes (analyte) to substrates bearing P-selectin (target). Commonly, such molecular binding occurs at sites of inflammation where carbohydrate ligands expressed on the leukocyte surface bind selectins expressed on the inflamed vessel wall (see figure below). This enables leukocyte recruitment at sites of inflammation, and the same process is also important during normal physiological immunity.
Experimental
Sensor Chip: Reichert Planar mixed SAM
Running Buffer: PBST
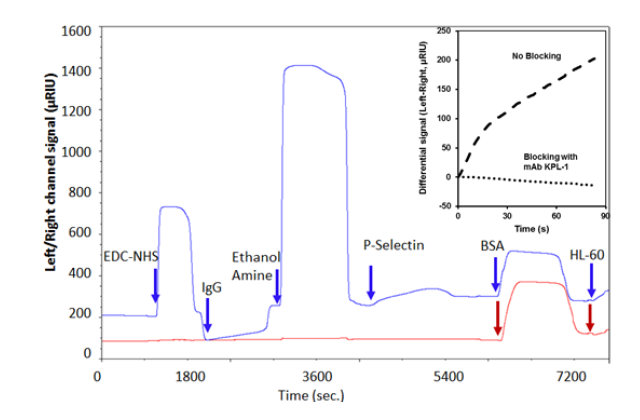
Anti-human IgG (MW 150 kDa, concentration 80μg/mL in pH 6.0 acetate buffer) was amine coupled to the left channel only by injecting for 10 minutes at a flow rate of 15 μL/min after EDC/NHS activation. Baseline increased by 200-250 μRIU. Recombinant P-selectin-Fc (5μg/mL; 10 min. capture at 15μL/min.; 240KDa) was then immobilized on the left channel to ~400 μRIU. This protein contains the N-terminal lectin binding domain of P-selectin fused to a human IgG1 Fc tail. Such immobilization is consistent with 1:1 antibody:protein capture interaction. Both channels were blocked with 2% BSA (Bovine Serum Albumin). Subsequently, 107/ /mL human leukocyte HL-60 cells were perfused in both channels at 50 μL/min.
Blocking studies were performed in some runs by incubating HL-60 cells with a blocking monoclonal antibody KPL-1 that binds the N-terminal portion of the glycoprotein ligand PSGL-1 (CD162, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1). This is the major ligand binding epitope of P-selectin on the human leukocytes.
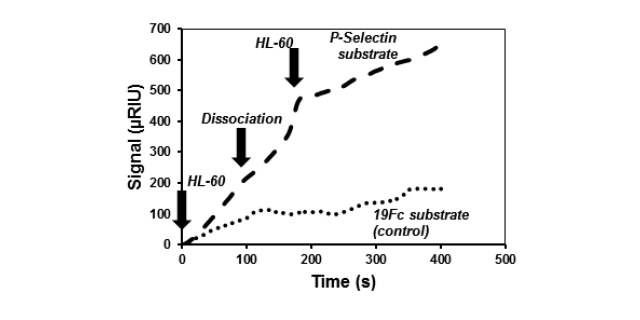
In other controls, the substrates contained a fusion protein called 19Fc, an irrelevant IgG1 fusion protein similar in all aspects to P-selectin-Fc except that the lectin-domain of selectins is replaced by 19 amino acids.
Results
Cell capture is noted in the left but not right channel in Fig. 1. Cell adhesion to immobilized P-selectin was prevented by the addition of the blocking antibody KPL-1 (inset to Figure 1).
When P-selectin-Fc was immobilized on the left channel and equivalent amounts of 19Fc were coupled on the right channel, cell adhesion was only noted on the left channel. This confirms the specificity of the measured interaction (Fig. 2).
Conclusions
- Results indicate that the measurement of cell adhesion can be easily performed using the 2SPR unit.
- Such assays will be helpful for studies of leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion and screening of related inhibitors.
- In general, the study demonstrates the ability to perfuse live cells and measurement of protein-carbohydrate interactions in the time scale of typical SPR runs.
- Following cell binding, cell spreading may be measured in the dissociation phase, where buffer is being perfused, in the absence of additional cells. In this way, SPR allows studies at short length and time scales that are not feasible using conventional light and fluorescence spectroscopy.
Potential opportunities/ Future directions
- While the current study examines binding to P-selectin versus a control substrate with no target-ligand, it is possible to immobilize another ligand like E-selectin in the second SPR channel. In this case, comparative time and spatial measurements of cell binding to two competing target-ligands can be measured simultaneously and quantitatively.
- Extension of the methods presented to other systems that involve cell adhesion like platelet adhesion under flow should be feasible.
- Methods to regenerate the sensor chip are important since this can enable reuse of the sensor chip for testing of different types of cells, combinatorial testing of drugs, and estimation of binding/unbinding rate constants.