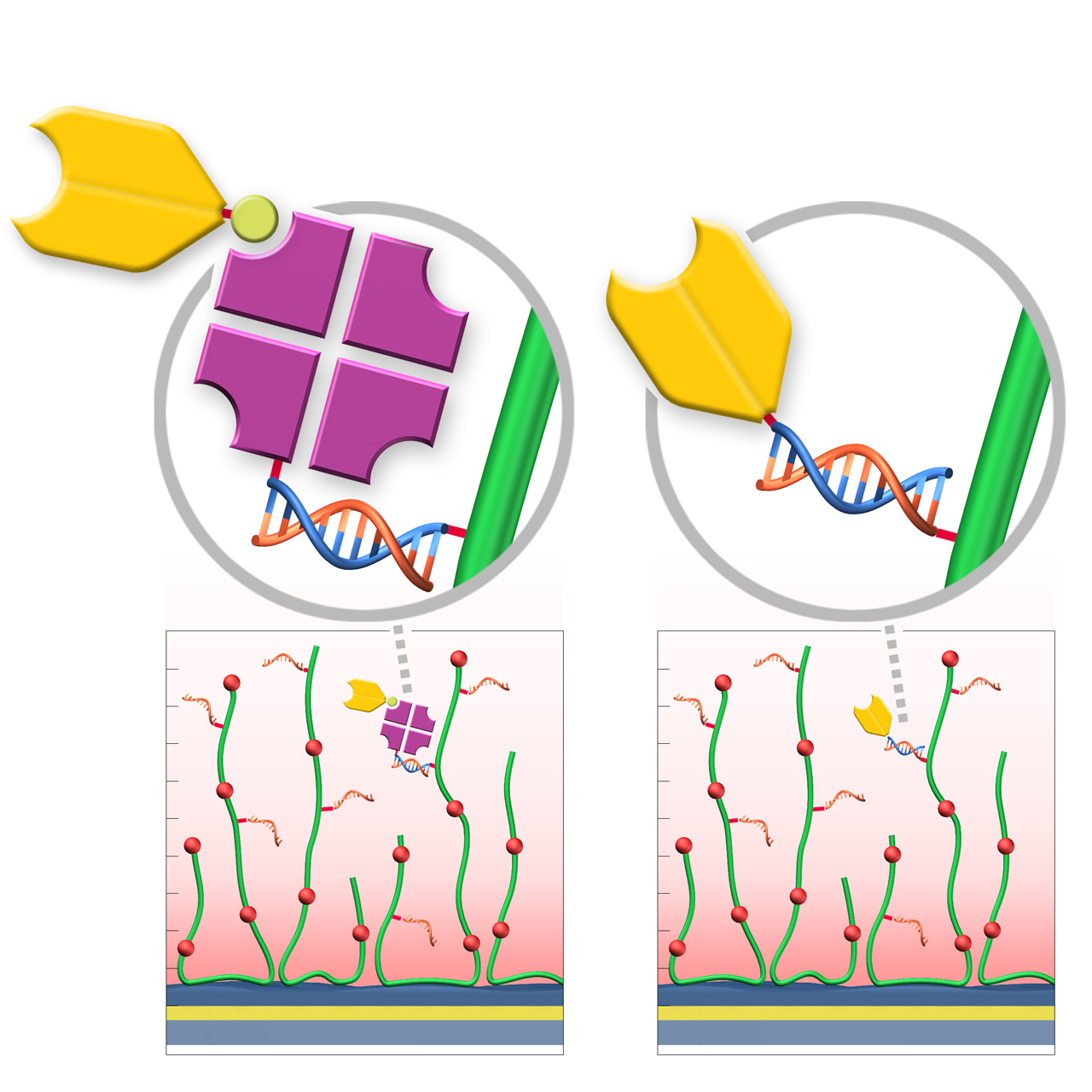
RG sensor chips (regenerable DNA-mediated capture)
XanTec’s RGD200M sensor chips are coated with a bioinert carboxymethyl-dextran matrix derivatized with a 24-nt single-stranded DNA oligonucleotide. This surface enables DNA-mediated, reversible ligand immobilization via hybridization with a complementary DNA sequence. Captured ligands are stably bound under physiological conditions, while quantitative regeneration is achieved by alkaline denaturation of the double-stranded DNA, restoring the surface for subsequent capture cycles.
Two complementary immobilization strategies are available. In Variant 1 (RG-SA), streptavidin pre-conjugated with the complementary DNA oligo is first immobilized via DNA hybridization, followed by capture of biotinylated ligands. In Variant 2 (RG-Modifier), ligands are directly conjugated to the complementary DNA oligo (e.g., via DBCO Click chemistry) and immobilized without an intermediate streptavidin step. Variant 2 can reduce nonspecific binding, lower diffusion limitations, enable higher capture densities, and facilitate faster assay setup.
Key features:
- Very fast assay development: No preconcentration, no surface activation, and no regeneration screening required; immobilization under physiological conditions.
- Maximum flexibility: Regenerable alternative to classic streptavidin/biotin capture immobilization.
- Exceptional stability: Drift-free immobilization of oligo-modified streptavidin.
- Simple regeneration: Quantitative regeneration enabling >100 capture/regeneration cycles.
- Oriented immobilization: Controlled biotinylation (e.g., AviTag™) supports high ligand activity and reproducibility.
- Ideal for large screening campaigns: Consistent surface performance across many cycles and sensor chips.
| Product code | RGD200M | RGD200M |
|---|---|---|
| Base coating | 3D, 200 nm bioinert CM-dextran (medium density) | |
| Variant | Variant 1: RG-SA | Variant 2: RG-Modifier |
| Capture immobilization capacity [µRIU] | ≈ 3,5002 | ≈ 5,0003 |
| Recommended ligands | biotinylated proteins or peptides | proteins or peptides with NHS-reactive amino groups |
| Recommended analytes |
|
|
| Intended purpose |
|
|
1 All illustrations are schematic representations and are not drawn to scale; dimensions, densities, and spatial relationships do not reflect actual physical or chemical proportions.
2 Based on capture of 100 µg/mL biotinylated BSA in PBS (RG-SA pre-capture), with 1 µRIU corresponding approximately to 1 RU.
3 Based on capture of 200 nM RG-SA on an RGD200M sensor chip.