Sensor chips with lipophilic anchors (HPP, LP and LD)
XanTec’s LP and LD sensor chips are coated with a bioinert 2D (CMDP) or 3D (CMD500L) carboxymethyl-dextran polymer matrix, partially functionalized with lipophilic alkyl anchor groups. In contrast to solely hydrophobic 2D chip surfaces such as HPP, LP and LD sensor chips are partially hydrophilic and conserve the functionality of lipid bilayer structures.
HPP sensor chips provide a dense 2D hydrophobic coating, which allows formation of stabilized lipid monolayers. The hydrophobic surface enables lipid monolayer adsorption for studying lipid-associated interactions.
LP sensor chips consist of a hydrophilic 2D CMDP cushion functionalized with lipophilic alkyl anchors. This architecture enables reversible adsorption and rupture of lipid vesicles, resulting in the formation of a supported lipid bilayer (SLB). Membrane proteins incorporated within vesicles typically remain structurally intact and maintain biological activity after bilayer formation, making LP chips suitable for interaction studies involving moderate- to high-molecular-weight analytes, such as proteins. LP surfaces also serve as robust supports for SLB model systems, offering multiple regeneration cycles.
LD sensor chips are coated with a hydrophilic, 3D hydrogel based on brush-structured carboxymethyl-dextran. Lipid vesicles can diffuse into the LD hydrogel matrix. Incorporation of the lipophilic anchor groups allows the reversible capture of such vesicles. The shape of the vesicles usually remains intact, making them suitable for biomolecular investigation of (trans)membrane proteins such as G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Compared to LP, the immobilization capacity of LD sensor chips is ≈ 50% higher, allowing investigation of biomolecular interactions, including smaller analytes.
Key features:
- HPP – Hydrophobic coating: Enables formation of a supported lipid monolayer; user-prepared liposomes adsorb and reorganize spontaneously into a monolayer with hydrophilic headgroups facing the bulk solution; not suitable for transmembrane proteins (risk of denaturation upon vesicle adsorption).
- LP – Supported lipid bilayer (SLB): Hydrophilic 2D coating with hydrophobic anchors supports reversible adsorption/rupture of vesicles and SLB formation; stabilization and preservation of (trans)membrane proteins for interaction analysis; regenerable surface suitable for multiple assay cycles.
- LD – Vesicle immobilization in 3D hydrogel: Hydrophobic anchors enable reversible immobilization of intact lipid vesicles and associated (trans)membrane proteins (e.g., GPCRs); higher immobilization densities support investigation of small analytes; regenerable surface enables multiple assay cycles.
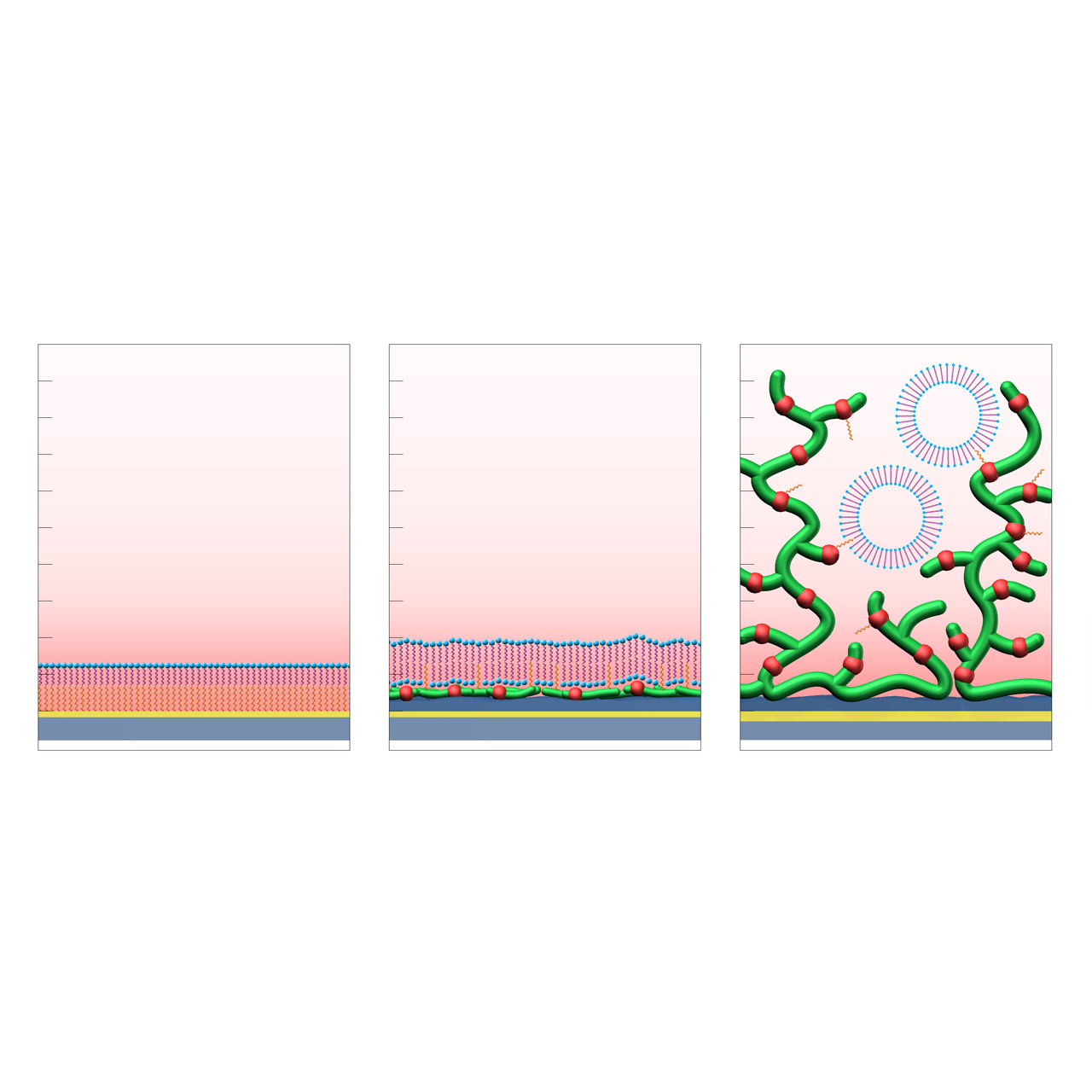
HPP (left): formation of a supported lipid monolayer (hydrophilic headgroups in blue, aliphatic tails in purple) on a hydrophobic planar self-assembled alkyl monolayer (SAM, orange).
LP (center): formation of a supported lipid bilayer on a hydrophilic CMDP base coating functionalized with hydrophobic anchor groups (orange).
LD (right): immobilization and stabilization of intact lipid vesicles within a 3D CMD sensor matrix modified with hydrophobic anchor groups (orange).1
| Product code | HPP | LP | LD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base coating | 2D, hydrophobic planar alkyl layer | 2D, carboxymethyl-dextran surface, partially alkyl-derivatized |
3D, carboxymethyl-dextran surface, partially alkyl-derivatized |
| Immobilization capacity [µRIU]2 | n. a. | ≈ 9,000 | ≈ 13,000 |
| Recommended ligands |
|
|
|
| Recommended analytes |
|
|
|
| Intended purpose |
|
|
|
1 All illustrations are schematic representations and are not drawn to scale; dimensions, densities, and spatial relationships do not reflect actual physical or chemical proportions.
2 Capacity determined by injecting an in-house vesicle formulation, with 1 µRIU corresponding approximately to 1 RU.