CMD–modified sensor chips
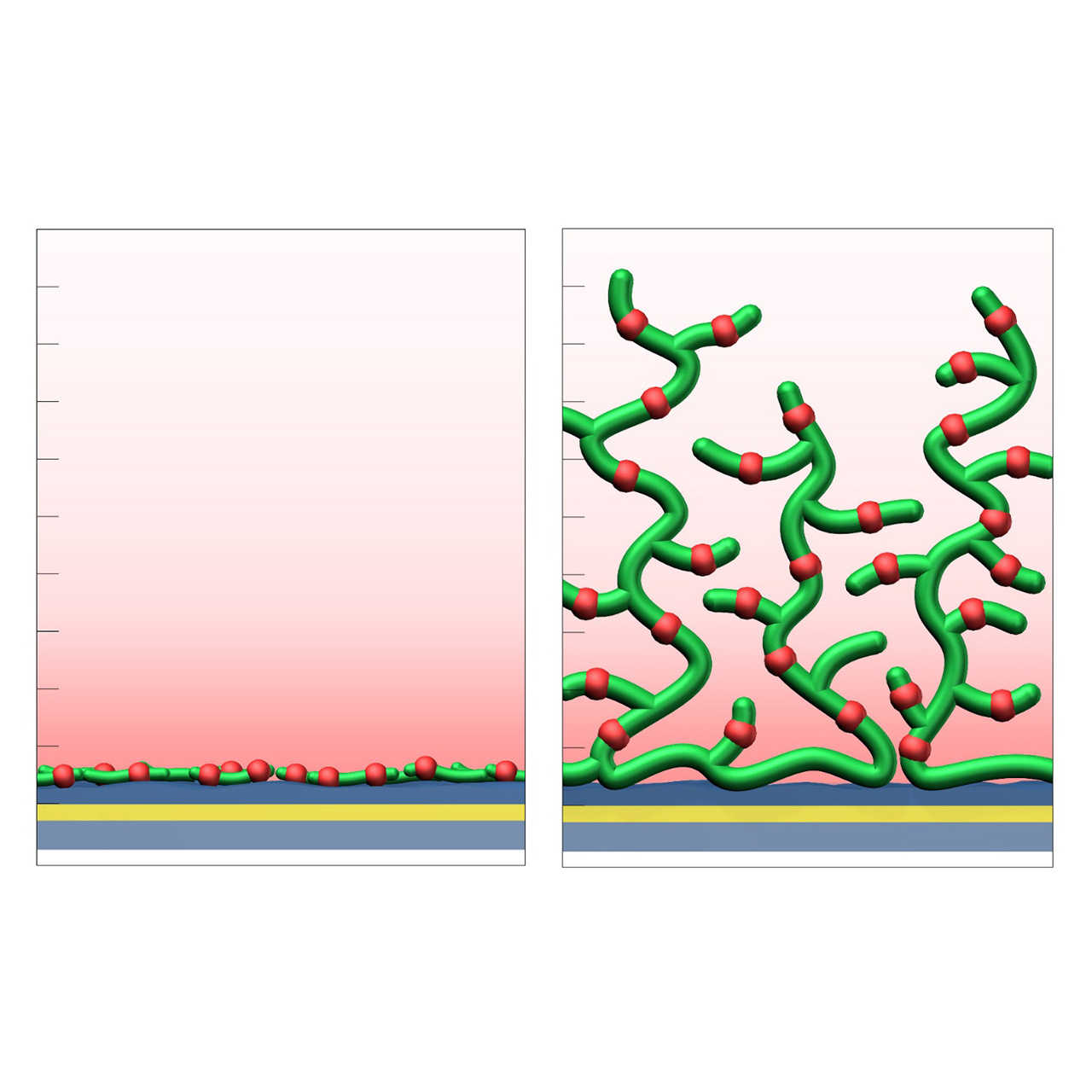
XanTec’s CMD sensor chips are based on a 2D (CMDP) or 3D hydrogel matrix consisting of carboxymethyl-dextran chains grafted onto a hydrophilic adhesion promoter on a gold support. Ligands can be covalently attached through their amine, thiol, or aldehyde groups using established coupling chemistries such as EDC/NHS activation, thiol-maleimide coupling, or reductive amination. This versatility enables the immobilization of a wide spectrum of biomolecules including proteins, antibodies, peptides, nucleic acids, and small organic compounds.
The CMD sensor chip portfolio spans electrostatic immobilization capacities from a few thousand μRIU (CMDP) to about 50,000 μRIU (CMD700M), covering analytes from large viruses to small organic fragments. Owing to this versatility, CMD chips are used in biochemical research, assay development, quality control, trace analysis, and drug discovery. Different chain densities further enhance flexibility:
- M variants (medium density, e.g., CMD200M, CMD700M) enable high ligand loading and elevated sensitivity for small-molecule kinetics and fragment screening.
- L variants (low density, e.g., CMD50L, CMD200L) occupy less of the evanescent field, minimize diffusion effects, and are ideal for capture assays or large analytes.
Key features:
- Versatile ligand coupling: Covalent coupling through amine, thiol, or aldehyde groups via standard chemistries (EDC/NHS, maleimide, reductive amination).
- Wide immobilization range: From several thousand to ≈ 50,000 μRIU, suitable for analytes from whole cells and viruses to fragments < 300 Da.
- Bioinert nanoarchitecture: Proprietary hydrophilic adhesion promoter combined with a hydrated CMD matrix minimizes nonspecific binding and matrix-analyte interactions.
- Application versatility: Suitable for kinetic, equilibrium, and concentration analyses, as well as diverse screening applications in drug discovery.
- High chemical stability: Withstands typical regeneration conditions, maintaining consistent response levels and kinetic behavior after multiple regeneration cycles.
| Product code 2 | CMDP | CMD50L | CMD200L | CMD200M | CMD700M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base coating | 2D, ultra-short bioinert CM-dextran (high density) | 3D, 50 nm bioinert CM-dextran (low density) | 3D, 200 nm bioinert CM-dextran (low density) | 3D, 200 nm bioinert CM-dextran (medium density) | 3D, 700 nm bioinert CM-dextran (medium density) |
| Immobilization capacity [µRIU] 2 | ≈ 5,000 | ≈ 10,000 | ≈ 22,000 | ≈ 33,000 | ≈ 50,000 |
| Recommended ligands |
|
||||
| Recommended analytes |
|
|
|
|
|
| Intended purpose |
|
|
|
|
|
1 All illustrations are schematic representations and are not drawn to scale; dimensions, densities, and spatial relationships do not reflect actual physical or chemical proportions.
2 This overview represents a selection of the full CMD sensor chip portfolio.
3 Preconcentration capacity determined by injecting 100 µg/mL bovine serum albumin (BSA) in 5 mM sodium acetate pH 5.0, with 1 µRIU corresponding approximately to 1 RU. Maximum covalent coupling yields can vary and depend strongly on the properties of the protein to be immobilized. Under optimal conditions, typical coupling efficiencies range from approximately 20–45% of the respective electrostatic preconcentration capacity, with acidic proteins generally exhibiting lower coupling efficiencies.